- Early Signs of Coeliac Disease
- How To Diagnose Coeliac Disease
- Coeliac Screen Blood Test
- Coeliac Blood Test Normal Range
- How Long Do Celiac Blood Test Results Take?
- Duodenal Biopsy
- Coeliac Disease Foods To Avoid
- Alternative Foods For Coeliac Disease
- Contact YorkTest For Help With Food Allergy and Intolerance Testing
Around 1 in every 100 people in the UK is affected by coeliac disease. That equates to approximately 670,000 individuals, and this number is expected to grow, with diagnoses increasing by an average of 7.5% per year in recent decades.
While awareness and diagnosis rates are improving, what’s surprising is that only around 36% of those with coeliac disease are currently diagnosed. This means that thousands may be unknowingly suffering in silence.
In case you’re not familiar, coeliac disease is a chronic autoimmune condition triggered by gluten: a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When someone with coeliac disease consumes gluten, their immune system reacts by damaging the small intestine. This impairs nutrient absorption and forces many to make significant lifestyle changes, including carefully checking ingredient labels and being extra cautious when eating out or ordering takeaway.
But it’s not all doom and gloom. Thankfully, living with coeliac disease today is far more manageable than it once was. There are now many excellent gluten-free alternatives and support resources available. It’s no longer a dietary death sentence; you can still enjoy a varied and satisfying diet, even after diagnosis.
At YorkTest, we’re passionate about spreading awareness of coeliac disease. In this guide, we’ll break down everything from screening and diagnosis to dietary decisions and daily living. We aim to show just how much support is available and how it continues to grow.
Early Signs of Coeliac Disease
Early signs of coeliac disease can be quite complex and hard to define. Some of the most common signs are gastrointestinal symptoms, such as:
- Persistent diarrhea
- Stomach aches and pains
- BloatingÂ
- Flatulence
Other, more general symptoms can include:
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Unintentional weight loss
- Mouth ulcers
- Neurological issues such as ataxia or peripheral neuropathy
Another potential early sign of coeliac disease that shouldn’t be ignored is its potential to delay growth or puberty in some children.
How To Diagnose Coeliac Disease
Diagnosing coeliac disease is usually done through a combination of blood tests and, if necessary, a duodenal biopsy.
Coeliac Screen Blood Test
A coeliac screen blood test is one of the most effective and popular ways to identify the disease in most individuals. The coeliac disease blood test is a key diagnostic tool that works by identifying specific antibodies in the blood that suggest a reaction to gluten.
The test primarily looks for IgA tissue transglutaminase (tTG) and IgA endomysial antibodies (EMA), which tend to be elevated in individuals with coeliac disease when gluten is present in the diet.
To ensure accurate results, it’s essential to continue consuming gluten regularly (typically in multiple meals each day) for at least six weeks before testing. Individuals with IgA deficiency may require alternative tests, such as IgG-based antibodies, for a more accurate diagnosis. If the test returns a positive result, there may be a need for further investigation, often including a referral to a gastroenterologist and potentially an intestinal biopsy, which is usually recommended to confirm the coeliac diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Coeliac Blood Test Normal Range
Normal results for a coeliac blood test typically include tTG IgA levels below 4 U/mL, EMA as negative, total serum IgA between 70–400 mg/dL, and DGP antibodies below 15 U/mL (lab-dependent). These markers help to assess the likelihood of coeliac disease and guide further testing if needed.
How Long Do Celiac Blood Test Results Take?
Typically, you will receive results from a blood test for coeliac disease within 1-2 weeks. However, it is always worth remembering that a positive test does not necessarily translate to a coeliac disease diagnosis.
Duodenal Biopsy
If the coeliac blood tests are positive or there’s strong clinical suspicion, a duodenal biopsy is often recommended to confirm the diagnosis. During the procedure, a thin, flexible tube (endoscope) is passed through the mouth to the small intestine, where a small tissue sample is taken from the duodenum. This sample is examined under a microscope to check for damage to the villi (the tiny structures that absorb nutrients, which is a key indicator of coeliac disease).
Coeliac Disease Foods To Avoid
If you have been diagnosed with coeliac disease, it is always advisable to be highly vigilant with the food you consume. Always double-check the labels to ensure you don’t accidentally consume gluten. Some of the most common foods you should avoid include:
- Grains – this includes wheat, barley, rye, bulgar wheat, couscous, and more. The same can also be said for products that are typically made from these grains, including bread, pasta, breakfast cereals, biscuits, crackers, cakes, pastries, pies, gravies, and sauces.
- Beers and Ales – unsurprisingly, if you enjoy an occasional pint of beer or ale and are diagnosed with coeliac disease, you may have to stop, as these beverages are often made with barley.Â
- Processed Foods – there are many processed foods, including meat substitutes, lunch meats, canned soups, and more, that may contain gluten.Â
- Some Flavoured Water and Drinks – even if you enjoy flavoured drinks, we regret to inform you that they can sometimes contain gluten or pose a high risk of cross-contamination.
- Some Sauces and Condiments – certain sauces and dressings can also contain gluten.Â
While these are some of the most common foods to avoid, if you or someone you know suffers from coeliac disease, then you need to be wary and check labels or ask the chefs who are preparing your food. It is best to be on the safe side.
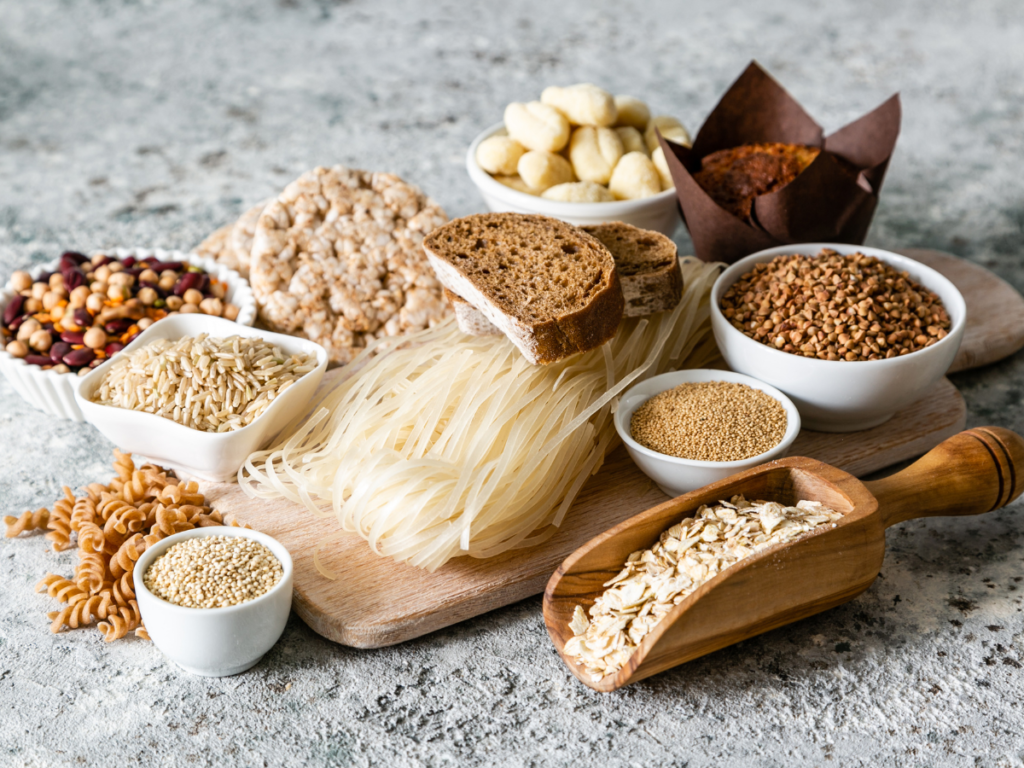
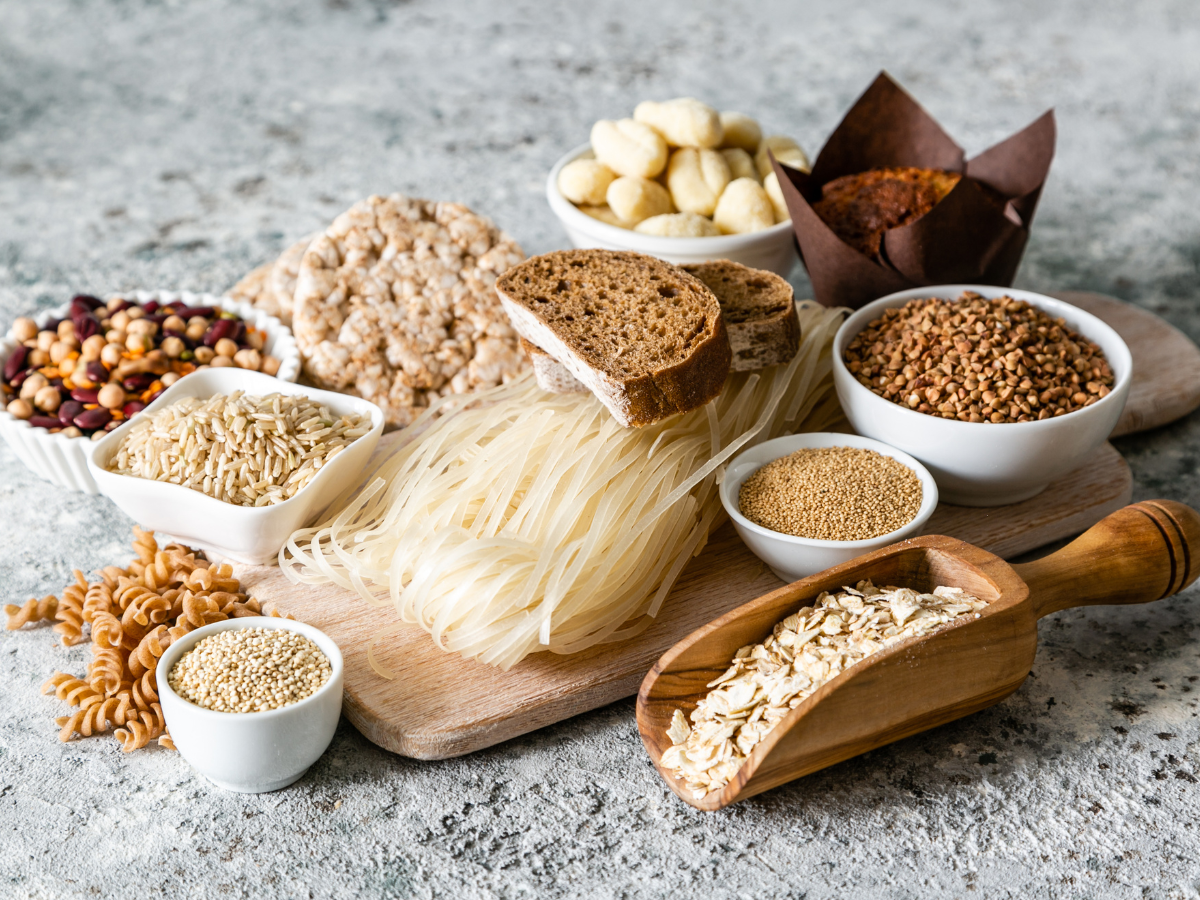
Alternative Foods For Coeliac Disease
Just because you have coeliac disease doesn’t mean you can’t enjoy some tasty eats; there are many gluten-free foods and gluten-free alternatives available, and these alternatives are becoming more and more prevalent. Some gluten-free foods include:
Most dairy products – such as cheese, butter, and milk.
Gluten-free flours – including rice, corn, soy, bean, and even potato flour.
Potatoes – while we’re on the topic of potatoes, they are also gluten-free.
Meat and fish – including steak, chicken (plain), fish, and more.
Rice – plain rice and rice noodles.
Fruit and veg – you can still get your five a day while sticking to a gluten-free diet.
Legumes – including beans, lentils, and peas.
Some alcoholic drinks – alcoholic drinks like wine, cider, and some gluten-free beers are OK in a gluten-free diet (in moderation).
Gluten-free cereals – just because you have coeliac disease doesn’t mean you have to swear off cereal completely. There are many cereals out there, and they are usually labelled as such.
Gluten-free pastas – pasta is another food that is made as a gluten-free alternative.
These are just some of the most popular gluten-free alternatives for those suffering from coeliac disease, but there are many more. Just because you have to adhere to a coeliac diet, it doesn’t mean you can’t still enjoy some of your favourite foods.
Contact YorkTest For Help With Food Allergy and Intolerance Testing
If you think you may have a food allergy or intolerance, please contact us at YorkTest. We can help you identify trigger foods and also assist you in removing them from your diet. This means you can enjoy a better quality of life and improve your overall well-being day-to-day. You can order one of our tests today, whether it’s our intolerance test, allergy test, or our combined package. If you have any questions about how to improve your diet and lifestyle, please don’t hesitate to contact us.